TripAdvisor is the most successful online forum in the travel and tourism industry. Easily the world’s largest travel community, it reaches 390 million unique visitors each month and lists 465 million reviews and opinions about more than 7 million accommodations, restaurants, and attractions in 49 markets worldwide.
Its recommendation algorithm provides a goldmine of data for analysts who work in marketing and are keenly interested in the opinions of consumers on the products and services they buy.
Analysts mine social media and other outlets for “sentiment analysis” and use that information to study what people like and don’t like—and, more importantly why—so that they can develop better marketing campaigns.
Researchers from the University of Granada have studied a number of web platforms and propose TripAdvisor as a highly valuable source for sentiment analysis.
Read TripAdvisor algorithm and sentiment analysis research here
Sentiment analysis is the process of computationally identifying and categorizing opinions expressed in a piece of text to determine whether the writer’s attitude toward a particular topic, product, or experience is generally positive, negative, or neutral, the authors say.
“The interest in sentiment analysis has increased significantly over the last few years due to the large amount of stored text in Web 2.0 applications and the importance of online customer opinions. As a result, more than 1 million research papers contain the term ‘sentiment analysis,’ and various start-ups have been created to analyze sentiments in social media companies,” the new study says.
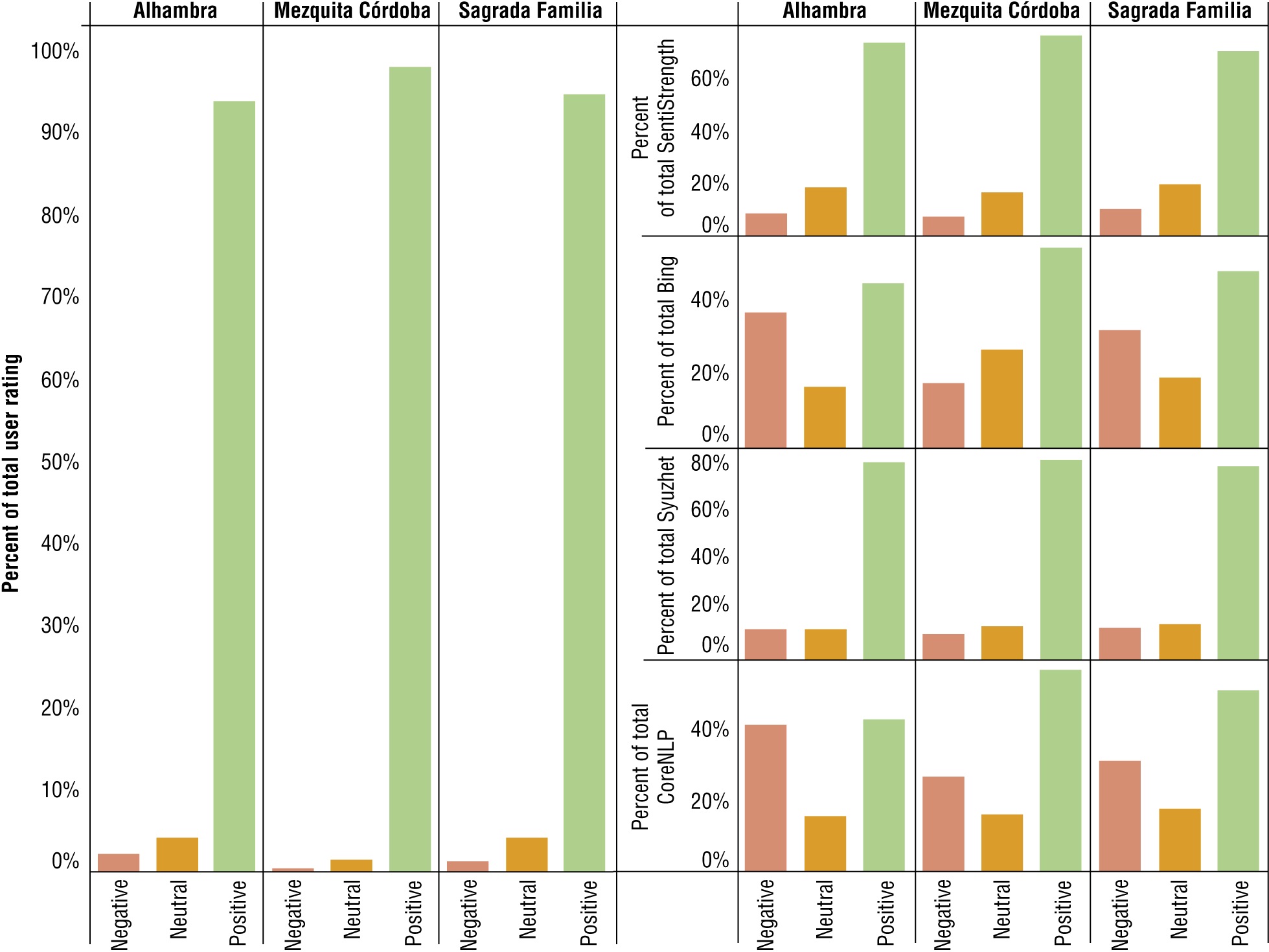
Distribution of sentiments between TripAdvisor users (bubble ratings) and four sentiment analysis methods (SAMs): SentiStrength, Bing, Syuzhet, and CoreNLP. Red indicates negative sentiments, orange neutral, and green positive.
“Multiple studies on TripAdvisor exist, but there is no complete analysis from the sentiment analysis viewpoint,” the report adds, written by Ana Valdivia, M. Victoria Luzón, and Francisco Herrera, all of the University of Granada in Spain.
TripAdvisor is a user-generated content website that “offers a plethora of reviews detailing travelers’ experiences with hotels, restaurants, and tourist spots. TripAdvisor has since been ranked as the most popular site for trip planning, with millions of tourists visiting the site when arranging their holidays,” the authors write in “Sentiment Analysis in TripAdvisor,” published in the July/August 2017 issue of IEEE Intelligent Systems.
The researchers developed an analysis for studying the matching between users’ sentiments and automatic sentiment-detection algorithms.
TripAdvisor’s sentiment analysis algorithm analyzes “sentiment polarity,” which labels reviews as simply good, bad, or neutral. Difficulties arise when the algorithm tries to scour the text for grammatical nuances, cultural variations, jargon, and misspellings.
Extracting accurate labels and fine-grained details from reviews is not as easy as it seems, but it is important because it reveals the reasons why reviewers may or may not like what is called an aspect.
“An aspect refers to an attribute of the entity, for example, hotel room cleanliness, the staff at a tourist spot, or the service at a restaurant. Aspect-based sentiment analysis aims to identify the sentiment toward an aspect and extract fine-grained information about specific TripAdvisor-based opinions (hotels, monuments, restaurants, and so on),” according to Ana Valdivia and her colleagues.
Other challenges include detecting irony/sarcasm in a post or review, which can make text appear negative when it is not, or detecting spam, which is not authentic.
While the research continues to evolve with regard to sentiment analysis, TripAdvisor gives researchers one of the most extensive databases of opinions to test new and better algorithms.
Despite some challenges with opinion summarization and opinion retrieval, the authors were bullish about how sentiment analysis is a growing field.
“The implementation of sentiment analysis techniques to mine sources of opinion is crucial to understanding the faults and assets of a tourist service. Given the large number of applications in the tourist domain, sentiment analysis has great potential to directly influence quality improvement in tourism,” the researchers say.
Research related to sentiment analysis in the Computer Society Digital Library:
- Affective Computing and Sentiment Analysis
- Statistical Approaches to Concept-Level Sentiment Analysis
- Semantic Multidimensional Scaling for Open-Domain Sentiment Analysis
- YouTube Movie Reviews: Sentiment Analysis in an Audio-Visual Context
- Knowledge-Based Approaches to Concept-Level Sentiment Analysis
Research related to transportation systems in the Computer Society Digital Library:
- Mapping Social Media for Transportation Studies
- Intelligent Transportation Systems
- Protecting Transportation Infrastructure
- Verification of Cyberphysical Transportation Systems
- RHODES to Intelligent Transportation Systems
- Navigation and Multimodal Transportation with EasyTransport
- The Growing Role of IT in Transportation
- Machine-Vision Systems for Intelligent Transportation Systems