As mass production goes global, industry leaders look to better forms of automation to increase efficiency.
However, many of them are moving back toward a human-centered framework because fully-automated systems are rife with error.
Machines are good at doing repetitive tasks much faster than humans. They are good at the heavy lifting. But sometimes, if assembly parts are not arranged in proper order, turned the wrong way, or missing altogether, the end product must be thrown out—costing the company time and money.
Like what you’re reading? Stay ahead of your field and sign up here for our Build Your Career or Computing Edge newsletters to get content like this delivered right to your inbox weekly.
So how can human and machine work together more efficiently?
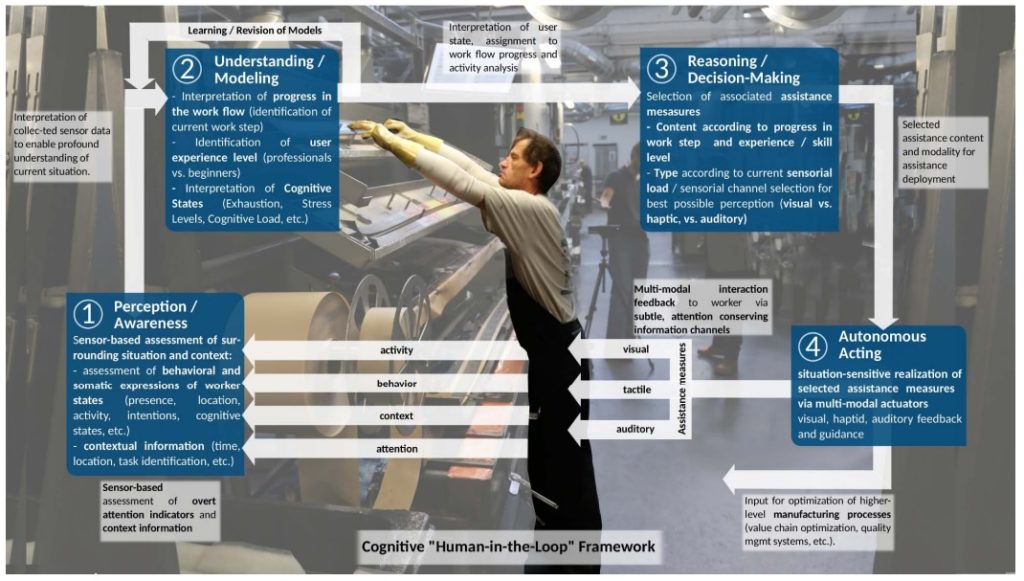
Schematic description of the proposed cognitive framework including the cognitive functions of (1) perception/awareness, (2) understanding and modeling of context, (3) reasoning and decision making, and (4) autonomous execution of assistance measures.
Researchers from Austria have developed a “cognitive assistance” framework for supporting human workers in industrial tasks—in their test case, assembly of an alpine sport product. The system is capable of detecting the steps in the assembly process, tracking the worker’s progress, assessing the mental and physical state of the worker, and determining the worker’s skill level.
With the human in charge, the computer system uses all of this information to provide support and correction if needed.
Read more in “A Cognitive Assistance Framework for Supporting Human Workers in Industrial Tasks.”